Listeners:
Top listeners:
00:00
00:00
volume_up
chevron_left
-
 play_arrow
play_arrow
Radio Today Radio Today
-
 play_arrow
play_arrow
Drivers Seat Motorsport Mike Stroud
-
 play_arrow
play_arrow
Drivers Seat Motorsport Mike Stroud

share
close
COPD – CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a serious group of lung conditions that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These conditions cause permanent changes in the lungs that make breathing more difficult.
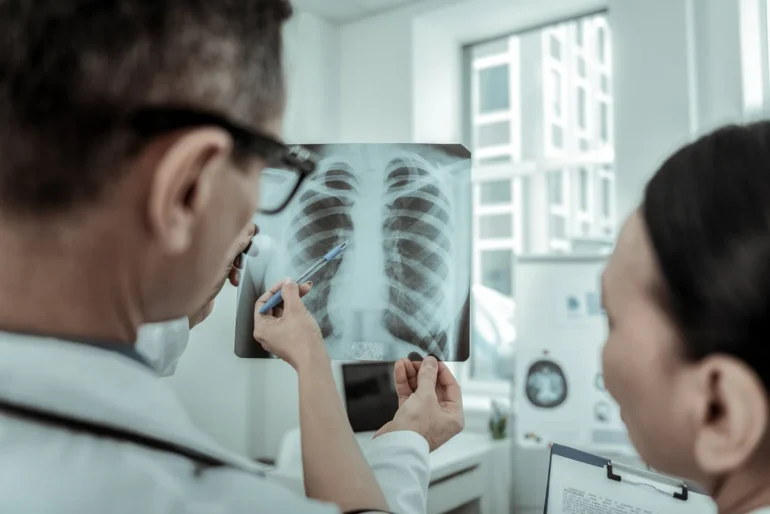
COPD may not always show up on an X-ray. However, when it does, doctors may notice visible signs, such as air pockets in lung tissue, a lowered diaphragm, or enlarged lungs.
Doctors may use CT scans instead of X-rays to get a clearer image of the inside of the lungs. CT scans can help doctors diagnose emphysema earlier and more effectively than X-rays. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are both types of COPD, but they cause different types of lung disease.
In chronic bronchitis, the airways are continuously irritated and inflamed, which leads to increased mucus production. In contrast, emphysema injures the small air sacs in the lungs, reducing the amount of oxygen they can exchange.
Doctors may order imaging tests, such as chest X-rays or CT scans to help diagnose COPD or monitor its progression. A chest X-ray may not show signs of COPD until the disease is severe. If changes are visible, they may include:
- Air pockets (bullae): These may develop when emphysema damages lung tissue. They reduce the usable lung space, making proper functioning difficult.
- Hyperinflated lungs: When the lung tissue sustains damage and loses its elasticity, it can expand significantly more than usual, leading to enlarged lungs. The lungs may also trap the air after each breath.
- Lowered, flattened diaphragm: This also results from hyperinflation, as the enlarged lungs push against the diaphragm, forcing it downward.
- Elongated heart: The heart may become longer as its position in the chest changes to make room for the expanding lungs. This may also occur due to a reduced volume in the left heart ventricle.
Emphysema causes more structural problems than chronic bronchitis, so these changes may be more apparent on an X-ray in a person with emphysema. However, if the person has chronic bronchitis, the bronchial walls may appear thicker than in healthy lungs. CT scans are often better at detecting visible signs of COPD and doing so at an earlier stage.
Chest X-ray vs. CT scans for COPD
A chest CT scan provides a more detailed view of the lungs than a chest X-ray, as it produces a three-dimensional view rather than a two-dimensional image.
An X-ray may identify an abnormality in an area of the lungs, but a chest CT scan can show the precise location and nature of the abnormality. CT scans can also identify emphysema more effectively and at an earlier stage than chest X-rays. Because X-rays typically cost less, doctors may first order an X-ray to help with a COPD diagnosis. Depending on what they find, they may then order a CT scan to get a more detailed view of the lungs.
A doctor may use:
Spirometry: Spirometry is the most common lung function test doctors use for COPD. It can detect COPD before symptoms show. The test measures how much air someone can breathe in and out of the lungs, and how quickly and easily they can breathe.
Peak expiratory flow test: This measures the maximum amount of air someone can blow out. A doctor may record it during a spirometry test.
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide test: This measures the amount of nitric oxide in the breath. A large amount of nitric oxide may indicate inflammation in the lungs.
Arterial blood gas test: This measures the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
COPD has no cure. The lung damage it causes is permanent and irreversible. However, treatment may slow the progression and reduce the symptoms. COPD causes progressive irritation and damage, which impairs the lungs’ ability to function. It cannot spread to other parts of the body.
Summary
Medical imaging scans of the lungs in a person with COPD may show visible air pockets, a lowered or flattened diaphragm, and lung enlargement. The heart may also appear elongated, and CT scans may detect enlarged arteries.
An X-ray may not show signs of COPD until the disease is more advanced. CT scans can often detect COPD earlier and more easily than other scans. Lung function tests, such as spirometry, can help doctors diagnose COPD before symptoms occur.
Although doctors cannot cure COPD, early diagnosis and treatment can help
prevent further damage to the lungs, slow the progression of the disease, and improve quality of life.
Last medically reviewed on May 27, 2025
Written by: Mike Stroud
Rate it
Similar posts
Recent Comments
No comments to show.Featured post

Latest posts
Current show
Upcoming shows

After Lunch with Radio Today
1:00 pm - 3:00 pm

Afternoons on Radio Today
3:00 pm - 6:00 pm

Motoring Today
6:00 pm - 7:00 pm

Your Classical Radio with Melissa Ousley
7:00 pm - 10:00 pm

BBC World Service
BBC World Service
10:00 pm - 11:59 pmChart